I Can Spell Electroencephalogram (EEG)
Recently, my neurologist ordered an EEG test for my epilepsy. EEG stands for electroencephalogram. An EEG records the electrical activity in your brain and it helps doctors detect abnormal electrical activity of the brain. Most types of EEG tests are considered relatively painless. However, like any medical test, from scheduling to prepping for the test, an EEG can always include some inconveniences and annoyances. Anyone who has ever had to remove EEG glue from their hair, understands why I call an EEG “relatively” painless.
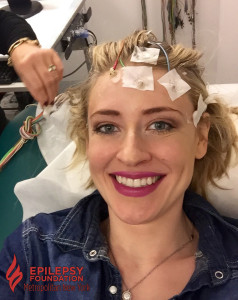
I had my first EEG test shortly after I was originally diagnosed with epilepsy when I was six years old. When my parents told me I had to undergo a new test related to my epilepsy, my first question was: “Are there any needles involved?” Luckily, my parents reassured me I would not be receiving a shot, getting an I.V. drip, or giving any blood. Plus, since my doctor prescribed me a sleep deprived EEG, the test prep required me to stay up late, preferably all night. Also, I got to miss a day of school, which was pretty cool! The next morning, my mother took me to my neurologist’s EEG lab. I was placed on a hospital bed and the technician glued electrodes to my head. After an hour of the technician asking me to breathe deeply and blink my eyes, they let me fall asleep. After I woke up, my electrodes were being removed from my head, and I returned home to go to bed. After several sleep deprived EEGs, I realized my mom also had to stay awake all night with me and miss work the next day. While I got to fall asleep for four hours during my EEG, my mom remained awake speaking with the technician or doctor. Now, as an adult, I understand how much an epilepsy diagnosis affects the entire family, from diagnosis to treatment.
In my twenties, I underwent a medication change because I began having a lot of seizures, again. My neurologist prescribed me several 72 hour ambulatory EEGs. For three days, I had a head full of glued-on electrodes. The electrodes were connected to wires, and the wires were connected to a small box recording the results. I could go anywhere, as long as I was still connected to my EEG box and electrodes. At work, I hid my electrode-covered head with a stylish beanie or scarf, allowing me to feel “normal.” Unfortunately, by the end of the first 48 hours, my head was itching like crazy. There was no beanie or scarf to alleviate my itchy head without removing the electrodes; but if these were to fall off, the EEG may have to be repeated! Finally, after the 72 hours, I would return to my neurologist’s office to have the electrodes removed.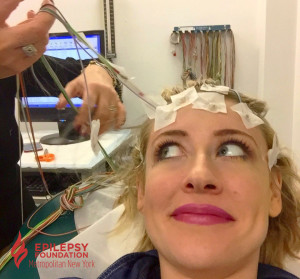
After any EEG, the inevitable issue of how to remove EEG glue arises. During this period of my life, I was not connected with the Epilepsy Foundation of Metropolitan New York, so I did not know the Epilepsy Foundation’s magic trick for removing EEG glue:
· Add 5 to 7 crushed aspirin to half a cup of hot water to dissolve. Then, add 2 good size squirts of shampoo, 4 tablespoons witch hazel or seabreeze, and mix well together. Massage the mixture through wet hair and let it sit for about 15 to 20 minutes. Finally, begin to comb through your hair after an allotted time has passed. Rinse and use shampoo and conditioner as usual.
I have never had to undergo a video-telemetry EEG test, which requires a patient to spend days in a hospital wearing an ambulatory EEG box, while being recorded by a video camera. Additionally, during a video-telemetry EEG test, epilepsy medications may be reduced or withdrawn, to increase the chances that you will have a seizure that can be recorded. So, while there are rarely needles involved, I would not dare to categorize all EEGs as “painless.”
 My recent standard EEG lasted for one hour and took place at my doctor’s office. It was the easiest EEG I had ever experienced. But, like epilepsy, even the types of EEG tests can vary. Like any medical procedure, it is important to stay informed and well prepared for an EEG test. The information an EEG test provides is essential for doctors treating epilepsy. Thankfully, this past EEG was totally painless because I finally knew how to remove EEG glue from my hair!
My recent standard EEG lasted for one hour and took place at my doctor’s office. It was the easiest EEG I had ever experienced. But, like epilepsy, even the types of EEG tests can vary. Like any medical procedure, it is important to stay informed and well prepared for an EEG test. The information an EEG test provides is essential for doctors treating epilepsy. Thankfully, this past EEG was totally painless because I finally knew how to remove EEG glue from my hair!
Infantile Spasms Awareness Week
Infantile Spasms (IS), also known as West Syndrome, is a rare form of age-specific epilepsy that usually presents itself in children within the first year of life. Early diagnosis and treatment of Infantile Spasms is of the utmost importance, and in many cases can ensure a more positive prognosis and a better quality of life, and significantly increases the chances of achieving reaching normal child development milestones.
Watch the videos below and check out our blog to hear a firsthand account of what it’s like to have a child with Infantile Spasms and to learn more about how Infantile Spasms (IS) are diagnosed, what signs to look for and what treatments are available.
In honor of Infantile Spasms Awareness Week, please share the videos below with friends and family in order to help us raise awareness about this rare form of epilepsy, and about the importance of early diagnosis and treatment.
Prognosis in Infantile Spasms – #EpilepsyNYC Infantile Spasms Awareness Week
Summary:
– The overall intellectual and neurodevelopmental outcome in children with infantile spasms is generally poor
– The long-term prognosis is directly related to the underlying cause of the seizures
– Better developmental outcomes are noted in patients without an identified cause (cryptogenic/idiopathic)
– Although the spasms tend to resolve by early to mid childhood, a majority of the children develop other types of seizures and epilepsies.
– There is a better outcome noted in those patients treated earlier in the course of their seizures, and in those that have an early and sustained response to treatment.

Infantile Spasms
The long-term prognosis of patients with infantile spasms has been studied extensively over the years. Many studies have examined the outcome of infantile spasms including neurodevelopmental and intellectual disabilities, prognostic significance of the EEG, and the development of chronic epilepsy.
The consensus of all of these studies is that the overall outcome, with regards to chronic epilepsy and neurodevelopmental disability is generally poor in patients with infantile spasms.
Chronic Epilepsy
Epileptic spasms usually resolve, latest by mid-childhood, in the majority of patients. Infrequently, spasms may persist in adulthood. Even if the spasms resolve, it has been found that 50-70% of the patients will develop other seizure types. Approximately 50% of the patients with a history of infantile spasms go on to develop chronic intractable epilepsy. There is a strong relationship seen between a history of infantile spasms (IS) and development of Lennox- Gastaut syndrome, with 18-50% of IS patients developing Lennox-Gastaut syndrome.
EEG
While features of hypsarrhythmia define the EEG of patients with infantile spasms, evidence of this abnormality on the first EEG was seen not to influence the response to treatment. However, if the hypsarrhythmia persisted despite treatment, or was atypical and/or asymmetrical, this was seen to adversely influence the long-term outcome.
Neurodevelopmental disability
The most important factor in predicting the cognitive and developmental outcome of patients is etiology.
Mental retardation occurs in about 70 % of patients with infantile spasms, usually involving severe to profound retardation and often associated with other psychiatric problems. Other neurological deficits, such as cerebral palsy, may be seen in about 30-50% of patients.
Most children with infantile spasms experience slowing, plateauing, or regression of their developmental progress.
Studies have consistently shown that infants with symptomatic infantile spasms are at much higher risk (86-90%) of developing mental retardation, autism and other behavioral and cognitive disabilities, compared to infants with idiopathic infantile spasms. Symptomatic infantile spasms, in particular, are associated with autism spectrum disorders (ASD) in up to 35% of cases.
10-20% of patients with normal development prior to the start of their spasms will have normal mental function or only be mildly impaired long-term. 28-50% of patients with idiopathic infantile spasms will go on to have normal or borderline cognitive development.
Mortality
The premature death rate for infantile spasm ranges from 5-31%. Most of the deaths (61%) occurred at or before age 3 years, while only 10% occurred after age 20 years.
In most cases, the mortality is seen to be a result of the underlying neurological cause of the infantile spasms.
Factors for a favorable outcome in Infantile Spasms
• Cryptogenic or idiopathic cause
• Age of onset of spasms > 4 months
• No atypical or partial seizures
• Typical EEG abnormalities – hypsarrhythmia
• Early onset of treatment
• Early and good response to treatment
Treating Infantile Spasms – #EpilepsyNYC Infantile Spasms Awareness Week
Infantile spasms is a potentially devastating early-onset epilepsy that affects infants, typically between three and nine months of age. Many cases of infantile spasms occur in children who are already have brain abnormalities, such as children with tuberous sclerosis, down syndrome, or brain injuries sustained as newborns. However, in about one third of affected infants, infantile spasms occur for no known reason.
There are three first-line treatments used for infantile spasms. Most pediatric neurologists select one of these three as the initial treatment.

First, adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) is a naturally occurring hormone that is made by the pituitary gland. It stimulates the body to produce steroids. There are several versions of ACTH available throughout the world — in the US, physicians can prescribe a pharmaceutical grade purified ACTH for infantile spasms. ACTH must be given by injection into the infant’s thigh twice a day for two weeks, and then gradually tapered over the next several weeks. There are significant side effects. Many babies become very irritable when taking this medication. It increases their appetite, and some gain weight during treatment. ACTH can also increase blood pressure and, on occasion, lead to an increase in the size of the heart. These side effects fade after the medication is stopped.
Second, oral prednisolone is a corticosteroid, which comes as a liquid. This is the same medicine given for children with asthma attacks; although, for infantile spasms we use a higher dose for a longer period of time (usually several weeks). It can have the same side effects as ACTH, but these are usually less severe.
Third, vigabatrin is a medication that comes as a packet of powder, which can be disolved in water. The major worrisome side effect of vigabatrin is loss of peripheral vision. This is uncommon. Usually when vigabatrin is prescribed, the infant will also need to see an ophthalmologist to monitor for this potential side effect.
Current evidence suggests that ACTH has the best overall response rate. The one exception is that for children who have infantile spasms due to tuberous sclerosis, vigabatrin seems to work better.
First-line therapy works between half and three quarters of the time. If it fails, there is not good evidence to guide us on what to try next. Many physicians will switch to a different first-line agent. For example, if a child continues to have seizures after ACTH, the physician may try vigabatrin next. Rarely, a deficiency of vitamin B6 can cause infantile spasms, and many physicians will give infants this vitamin. Other physicians may try dietary therapy. For example, there is a diet called “the ketogenic diet” that avoids carbohydrates and sugars. This diet can lead to changes in how the brain makes fuel for itself, which can, in turn, reduce seizures.
In some cases, children with infantile spasms may have a subtle area of the brain which is abnormal, which is difficult to see on MRI scans. Some physicians will order other kinds of brain scans, such as a PET scan (positron emision tomography), in order to look for these kinds of abnormalities. This is important, because some infants benefit from epilepsy surgery to remove the abnormal area of brain.
Dr. Zachary Grinspan, MD
Weill Cornell
SUDEP Awareness Day 2015
What is SUDEP?
Sudden Unexpected Death in Epilepsy (SUDEP) is said to occur when a person with epilepsy dies unexpectedly and was previously in their usual state of health. The death is not known to be related to an accident or seizure emergency such as status epilepticus. When an autopsy is done, no other of cause of death can be found. Each year, more than 1 out of 1,000 people with epilepsy die from SUDEP. However, it occurs more frequently in people with epilepsy whose seizures are poorly controlled.
The Epilepsy Foundation’s SUDEP Institute works to prevent Sudden Unexpected Death in Epilepsy (SUDEP) and support people confronting the fear and loss caused by SUDEP.
How common is SUDEP?
- Each year, more than 1 out of 1,000 people with epilepsy die from SUDEP. However, it occurs more frequently in people with epilepsy whose seizures are poorly controlled.
- One out of 150 people with poorly controlled epilepsy may die from SUDEP each year.
- SUDEP takes more lives annually in the United States than sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS).
- Most importantly, SUDEP is the leading cause of death in young people with certain types of uncontrolled epilepsy.
Who is at risk for SUDEP?
The greatest risk factor for SUDEP is frequent seizures, especially generalized tonic-clonic (grand mal) seizures. Other risk factors being looked at include:
- Epilepsy beginning at an early age
- Having epilepsy for a long time
- Not taking medications regularly or as prescribed
- Stopping or changing medications suddenly
- Young adult age (20-40 years old)
- Intellectual disability (IQ<70)
How can one reduce the risk?
The best way to prevent SUDEP is to have as few seizures as possible. Get the best seizure control possible. This may involve actions such as:
- Taking medication regularly and at the right dose.
- Visiting your health care team regularly, especially if seizures are not controlled.
- If medicines do not work, consider other therapies such as epilepsy surgery, vagus nerve stimulation, or dietary therapy.
- Take good care of yourself or your loved one. Eat well, get enough rest and regular exercise, avoid drinking too much alcohol or using recreational drugs, and minimize stress when possible.
- Be aware of and avoid any potential seizure triggers whenever possible. Keep a record of things that occurred before a seizure (such as illness, tiredness, stress, missing medications, and where and when the seizure occurred).
- Talk to your doctor about having your heart checked (cardiac evaluation) to rule out any heart problems. This is particularly important for people with uncontrolled epilepsy who don’t have a cause for their epilepsy found on an MRI or other type of imaging study.
- Be seizure safe. Make sure family and co-workers know what to do for seizure first-aid, take extra precautions around water, including swimming and bathing.
Speaking with your doctor about SUDEP?
If your doctor has not spoken to you about the health risks associated with epilepsy, you should ask him or her about SUDEP. Questions to ask may include:
- What risks do I or my family member have for SUDEP?
- What can we do to lessen the risk of SUDEP?

Source: EFA – SUDEP
Studio E for Teens NYC – Art Therapy
The Epilepsy Foundation of Metropolitan New York is excited to announce the first ever Epilepsy NYC Studio E Art Therapy for Teens!
Made possible through the generous support of Lundbeck, Studio E offers a unique way for people with epilepsy to socialize with others and open up honestly about daily challenges in a trusting, creative environment. Art therapy promotes self-expression and builds confidence. Recent studies have shown that Studio E improves quality of life and
self-esteem.
After the great success of the Annual Studio E Program hosted by EFMNY and supported by well-received public exhibitions, Art Therapist Melissa Diaz joins us once again to provide an 8-session group program, in the same open studio model, but now tailored specifically for teenagers with epilepsy.
WHO: Teens ages 15-19
WHEN: Tuesdays after school beginning in late October 2015
(8 sessions)
WHERE: Mount Sinai Beth Israel’s PACC at Union Square
To enroll or learn more please contact Katie Lorenzo at klorenzo@efmny.org or call us at 212-677- 8550.
The program is offered at no cost to participants. You must be 15-19 years old. Seating is limited and a phone interview with the art therapist is required.

